GROW YOUR BUSINESS THROUGH EXPORT OF GOODS AND SERVICES
By Ayoade Apelegan
INTRODUCTION
International trade is important in the expansion of the economy of a country because it allows for the development of markets, creates employment, reduces the rate of poverty, and breaks monopolies by discouraging the domination of a market by a few.
The rise in the non-oil product export sector is rapidly growing on the hills of the crude oil price crash and the current Federal Government’s policy and support for the non-oil industry.
As at the last count Nigeria exports over 120 products to different countries. While raw commodities still dominate the market in terms of volume of export, small scale export is gradually improving it stalks in value-added products as a result of new rules from foreign countries concerning the import of food items from Nigeria.
PROCESS OF EXPORT IN NIGERIA
Registration of Business Name:
The exporter must be a registered/incorporated business in Nigeria.
Whenever one decides to start a business, registering the business is the first thing to do. It saves one from a lot of legal issues when one registers the company.
Registering a company, in simple terms, means letting the government know you now own a business and that your business name is yours.
The Corporate Affairs Commission is the Agency authorized by the Company and Allied Matters Act 1990 to register businesses in Nigeria
E-REGISTRATION
For anyone willing to export from Nigeria, such person is required to register with the Nigerian Export Promotion Council (NEPC). Registration as an exporter can only be done using the e-registration platform. The page contains all the required information needed to obtain an Exporter’s Certificate.
Benefits of registering with Nigerian Export Promotion Council
- Trade promotion support services
- NEPC administered (pre- and post-) export incentives
- Numerous training, clinics, seminars, and more
- A network of exporters to collaborate and exchange ideas.
Guidelines & procedures
There are documents required for completing the registration process. The documents depend on the type of company involved in the export process.
DOCUMENTS FOR LIMITED LIABILITY COMPANY
- Certificate of Incorporation (issued by the Corporate Affairs Commission)
- Certified True Copy of Memorandum and Articles of Association
- Current Certified True Copy of Form CAC 1.1 – “section C” (Particulars of Directors).
DOCUMENTS FOR CO-OPERATIVE SOCIETY
- Certificate of Registration (issued by State Ministry of Commerce, Local Governments and Federal Capital Territory Area Councils)
- Bye-Laws of the Society
DOCUMENTS FOR GOVERNMENT AND NON-GOVERNMENT ORGANIZATION
- Certificate of Registration (issued by the Corporate Affairs Commission)
- Constitution of the Government Organization and non-Governmental Organization
- Memorandum for Guidance of Applicant
Fees & Charges
The following are the costs associated with obtaining an exporter’s certificate excluding bank charges.
- New certificate registration – ₦13,500
- Expired certificate renewal – ₦7,500
- Late certificate renewal (after Three months of expiry) – ₦12,500
- Lost/mutilated certificate – ₦12,500
Payment can be made through the following channels
- Nigerian local cards
- International credit / debit cards
- Internet banking
- Commercial bank branches in Nigeria
(Note: The e-registration platform was launched on the 3rd of April, 2017 and only companies registered after this date will be eligible for renewals. All companies registered before this date with expired certificates will need to migrate to the new platform by registering afresh for a new certificate.)
Payment confirmation
After payment for registration, confirmation of payment can always be done by:
- Copying the Order ID from your certificate (see Transactions Log)
- Input it in the field beside “Get Status”
- Click on Get Status to confirm your payment
- You will receive a notification of the status of your payment
Service timeline
The Nigerian Export Promotion Council aims to issue certificates within one working day after payment is confirmed by the system. It should be noted that issuance of certificates could be delayed by late payment confirmation, issues with documents or insufficient information supply.
(Source: www.nepc.gov.ng)
EXPORT INCENTIVES
There are certain export incentives attached to being an exporter in Nigeria. These incentives range from monetary, tax or legal provisions designed to encourage export of certain goods and services. The incentives are provided to help exporters in keeping their products competitive in global markets.
Two export incentives being administered by NEPC are:
- Export Development Fund
- Export Expansion Grant. Find out more about these incentives
Advantages of these incentives are:
- The provision of financial grants allows the exporter to expand exports more easily
- Cost of production support makes products more competitive in global markets
- Financial support facilitate greater / faster market penetration
(Source: www.nepc.gov.ng/trade-facilitation/export-incentives/)
EXPORT SUPPORT PROGRAMMES
The Nigerian Export Promotion Council (NEPC) offers numerous export support programmes throughout the country for Nigerian exporters. These are intervention programmes aiming to enhance product quality (focused on specific sectors). Through capacity building and infrastructural provision, the NEPC helps to build and increase competitiveness in international markets.
There are no costs attached to the export support programmes.
However, there are selection procedures. To participate in any of these programmes, all an exporter has to do is register online with their company profile. Selection is done based on the information provided.
Examples of the support programmes are:
- The Human Capital Development Centre (HCDC) – is based in Lagos offers short-term skill acquisition. It is a very well-equipped programme centre for companies active in the apparel and garments sector. The programme supports companies to become competitive in international markets. This is done via training in the areas of entrepreneurial skills, designing, production, packaging and marketing.
- Common Facility Centre (CFC) – The Council established a Common Facility Centre in Aba to ensure that Nigeria made shoes meet international standards with requisite modern machines needed to produce shoes and leather products. The project is a joint programme of NEPC and United Nations Industrial Development Organisation (UNIDO), Federal Ministry of Trade and Investment (FMITI) and the Abia State Government. The setting up of the CFC was to gather the sectoral and geographical concentration of enterprises, faced with common opportunities and challenges and with the primary objective of exploiting external economies through collective effort and sharing common facilities for enhanced processing of their products. The centre is equipped with various types of sewing machines, trap folders, folding machines, eyelet presser for shoelace, smoothing machine, nailing machine as well as cooling and cementing machines.
UNDERSTANDING THE MARKET
To develop your export business into a success, you need to ensure that you understand your target market(s).
This involves researching your export destination(s).
Good market research isn’t all about assembling facts and figures, it should focus on what drives the target market(s) and how to get the best out of it.
Tips for understanding the market
- Gather basic market information, from import regulations to trade statistics. You can make use of available Market Analysis tools.
- Narrow the focus of your research to your product or service to make it more specific.
- Research competitor markets. (Find out what they are doing right and how they are doing it)
- Attend market-specific seminars
- Seek practical advice from experienced exporters
- Develop direct contacts with potential buyers. (You can make use of several online directories)
- Understand the market environment. (Relevant Trade Fairs and Embassies are good sources of information)
Research Areas
Some of the important areas of market research include:
- Trade statistics and trends
- Trade policies
- Regulatory framework
- Business environment
- Business culture
- Distribution channels
- Trade logistics
- Risk assessment
Tools for Market Analysis
There are numerous online Market Analysis tools available. Some of these tools can be accessed for free. These tools will enhance the understanding of your target market(s). Examples of Market Analysis Tools are:
Export Potential Map
The Export Potential Map translates rigorous trade analysis into practical information about export opportunities for over 4,000 products. Based on an economic model that draws on trade, tariff, GDP and geographic data, the tool helps countries spot untapped export potential as well as opportunities for export diversification.
Trade Map
Trade Map provides online access to one of the world’s largest trade databases. It presents indicators on export performance, including yearly export/import values and volumes, (average) annual growth rates, and more based on customs data around the world. Therewith you can generate international demand, alternative markets and the role of competitors from your perspective. Tip: register for free to get access to all available data.
Market Access Map
Market Access Map provides information on applied customs tariffs, including Most Favoured Nation (MFN) tariffs and unilateral and trade agreement preferences. The application also covers tariff rate quotas, trade remedies, rules of origin, plus the corresponding certificates, bound tariffs of World Trade Organization (WTO) members, non-tariff measures and trade flows.
Sustainability Map
The Sustainability Map provides online access to a wide range of information related to sustainability initiatives, standards and trends, allowing businesses to deploy better sustainability practices in international trade. It includes global sustainability standards requirements and clarifies all types of relevant standards in international markets.
Product Specific Market Research
Having gathered and analysed basic information, narrow down the research to your specific product or service. Gather feedback on your offer by sending data or samples to buyers. Pay attention to analysing the competitors of your target market(s) in this stage.
International Buyer Directories
There are several international buyer directories available (some free, others require paid subscriptions). Most of them can be found on the internet
Benefits of Market Research
Good market research enables you to:
- Identify your most promising market
- Obtain inputs for your export plan
- Have a good understanding of the competitive landscape of your target market
- Minimize risks and maximize prospects
EXPORT PLAN
After you might have researched the market opportunities, selected your target market(s) and gathered information concerning these market(s) it is time to develop an export plan.
Five export plan tips
- Keep your plan simple and to the point
- Always include your unique value proposition (this describes what differentiates you from your competitors)
- Always develop a very concrete budget plan
- Keep your target market in mind when defining your export plan
- A good export plan guides you seamlessly through different export processes. It helps when you are in touch with financial advisers, brokers and governmental bodies
Benefits
A well-written export plan will assist in defining export goals and match your resources to those goals. Focusing your resources allows you to provide excellent service delivery to your clients (importers). It makes your company stand out, projecting it as one that has realistic goals with outlined plans on how to achieve them. Finally, it will guide management on long-term commitment for exports.
Key elements
A good export plan consists of certain key elements. NEPC developed a guideline on the export plan for exporters. This includes the following key topics:
- Company profile (about us)
- Key features of the target market(s)
- Competitors’ analysis
- Market entry strategy
- Unique selling points
- Promotional strategy
- Branding (if relevant)
- Logistical planning
- Action plan
- Resources required
Export plan template
NEPC has provided a template containing all the key elements listed above and includes additional descriptions per element. It guides you to build your own comprehensive and complete export plan.
The image below (source: www.nepc.gov.ng) shows an example of the export plan template.
EXPORT DOCUMENTS & PROCEDURES
Documentation is of utmost importance in the business of export. Much reliance is placed on documents related to price, quantity, packaging, shipment/movement, origin etc., in a bid to confirm adherence to stipulated procedures.
The buyer needs the documents that would enable him to clear the goods in his country while the seller/exporter needs the documents to ensure that he will get paid.
REQUIRED EXPORT DOCUMENTS
The following documents will be required at different stages of the export process.
EXPORTER REGISTRATION DOCUMENT
To venture into the export business in Nigeria, the first step of the export procedure is getting registered as an exporter with The Nigerian Export Promotion Council (NEPC).
EXPORTER’S CERTIFICATE
This is issued after registration by NEPC.
The exporter’s certificate licenses you as an exporter and makes you eligible for NEPC benefits.
To obtain this document, kindly visit -> (www.nepc.gov.ng/get-started/e-registration/)
EXPORT CONTRACT DOCUMENT
An export contract can be defined as an agreement between a seller and a buyer on the terms of export business.
The export contract document spells out the obligations of both the buyer and the seller.
This document is issued by the exporter and the importer.
QUALITY ASSURANCE DOCUMENTS
Quality assurance documents are documents that help to ensure exported goods conform to safety measures (as stated by agreed terms of the contract and international conventions). Using international recognized bodies is very important.
Relevant quality assurance documents include:
A phytosanitary certificate for agricultural, animal and plant commodities issued by Nigeria Agricultural Quarantine Service (NAQS).
Health certificate for processed and semi-processed food items issued by the National Agency for Food and Drug Administration and Control (NAFDAC)
International veterinary certificate for animals and animal products issued by The Department of Veterinary and Pest Control Services (DVPCS)
Fumigation certificate for agricultural commodities issued by Federal Produce Inspection Service (FPIS) which is an arm of The Federal Ministry of Industry and Investment (FMITI)
COMMERCIAL DOCUMENTS
The commercial documents display product values and quantities. The documents are both prepared and issued by the exporter and include:
Proforma Invoice: An offer by an exporter to sell specified goods for a certain price and at certain terms in a formal manner.
Commercial Invoice: This indicates the value of goods for export in the currency of the transaction.
Packing List: This indicates the unit packaging and total quantity of goods intended for export.
FINANCIAL DOCUMENTS
The preparation of financial documents shows evidence of a financial transaction between a buyer and a seller. It also shows conformance with the financial regulation for exports. Examples of financial documents are
Nigeria Export Proceed Form (NXP Form): This is a document that is required to be completed by all exporters for shipment of goods outside Nigeria.
This is issued by commercial banks. It captures the value of the export transaction for economic development purposes. It is also a major prerequisite for accessing the Export Expansion Grant (export incentive).
Commercial Invoice
This is issued by the exporter. It shows the value of the goods for export in the currency of the transaction. It is also useful for processing the NXP
Final Invoice: This is issued by the exporter. It indicates the actual value of the goods exported in the currency of the transaction. This for payment by the importer.
GOODS MOVEMENT DOCUMENTS
This deals with all aspects of the delivery of goods to the buyer in the medium specified in the export contract.
Below are some Goods Movement Documents:
Clean Certificate of Inspection (CCI)
This is issued by government-appointed Pre-Shipment Inspection Agencies (PIAs).
It ascertains the quality, quantity and price competitiveness of Nigerian exports.
Certificate of Weight and Quality
Certificate of weight and quality is issued by independent quality assessors (e.g. SGS, Bureau Veritas) that have been agreed by seller and buyer.
This is to ensure the goods conform to the quality standards and weight as stated in the contract.
Certificate of Origin
The Certificate of Origin is issued by the National Association of Chambers of Commerce, Industry, Mines and Agriculture (NACCIMA).
This certificate indicates the origin of the goods being exported.
Bill of Lading (shipping document)
This is issued by the shipping agencies. It indicates the details of goods transported by sea.
Air Way Bill (shipping document)
This is issued by airlines. It indicates the details of goods transported by air.
Road Transport Bill (shipping document)
Road transport bill is issued by logistics companies. It indicates the details of goods transported by road.
Benefits of Export Documentation
- minimizing export risks
- ensuring that exported goods conform to importing country specifications
- meeting buyer requirements for export by providing evidence of origin and delivery
- support to formalize export business
- support in qualifying for export incentives
Having completed the NXP Form, the exporter shall collect a REQUEST FOR INFORMATION (RFI) Form from the Inspection Agent or download from the Inspection Agent’s website. The purpose of the RFI Form is to enable the inspection company to coordinate with the exporter, a suitable time and place for the physical inspection. It is therefore essential that exporters provide in the RFI, all the required information promptly.
However, some goods are exempted from inspection.
SCHEDULE ‘A’ EXPORT GOODS EXEMPTED FROM INSPECTION
- Personal effects
- Used motor vehicles
- Perishables i.e. day old chicks, human eyes, human remains, vaccines, yeast.
- Periodicals/magazines
- Object of art
- Explosives
- Pyrotechnic products
- Arms
- Ammunition
- Weapons
- Implements of war
- Live animals
- Household and other non-commercial products including Gifts and personal effects, trade samples/printed business matter, machinery and equipment for repairs abroad, machinery for the execution of a specific contract, re-exports, Return of empty containers
- Transshipments
- Supplies to Diplomatic/Consular Missions and supplies to UNO for their own needs.
EXPORT PROHIBITION LIST
- Maize
- Timber (rough or sawn)
- Raw hides and skin (including Wet Blue and all unfinished leather) HS Codes 4101.2000.00 – 4108.9200.00
- Scrap Metals
- Unprocessed rubber latex and rubber lumps
- Artefacts and Antiquities
- Wildlife animals classified as endangered species and their products (e.g. Crocodile, Elephant, Lizard, Eagle, Monkey, Zebra, Lion etc.)
- All goods imported
(Source: www.customs.gov.ng)
LOGISTICS & FREIGHTS
When exporting ensure you understand the basic terms of shipping (including pricing and documentation). You must also understand the responsibilities of the major players for the safe delivery of your products to buyers. Such details include the duration of shipment, transport modes, conditions required for different products and the agreed terms of trade.
Five tips
Understand the importance of freight forwarding for a seamless export process
Know the available range of logistics options
Conduct due diligence in engaging a freight forwarder
Know how to apply INCOTERMS (2010) to quote your price for delivery correctly
Familiarize yourself with export documents and documentation process for logistics
Freight forwarders & Custom Brokers
You must identify experienced custom brokers and freight forwarders. This would ensure that your products get to the buyer via the most appropriate conditions, costs and routes. Familiarize yourself with different transport modes required to deliver the goods to the buyer. To be well prepared please:
conduct research on at least three freight forwarders/custom brokers
visit the online database of freight forwarders, customs brokers and cargo agents in Nigeria
Read on How to Manage Business Inventory
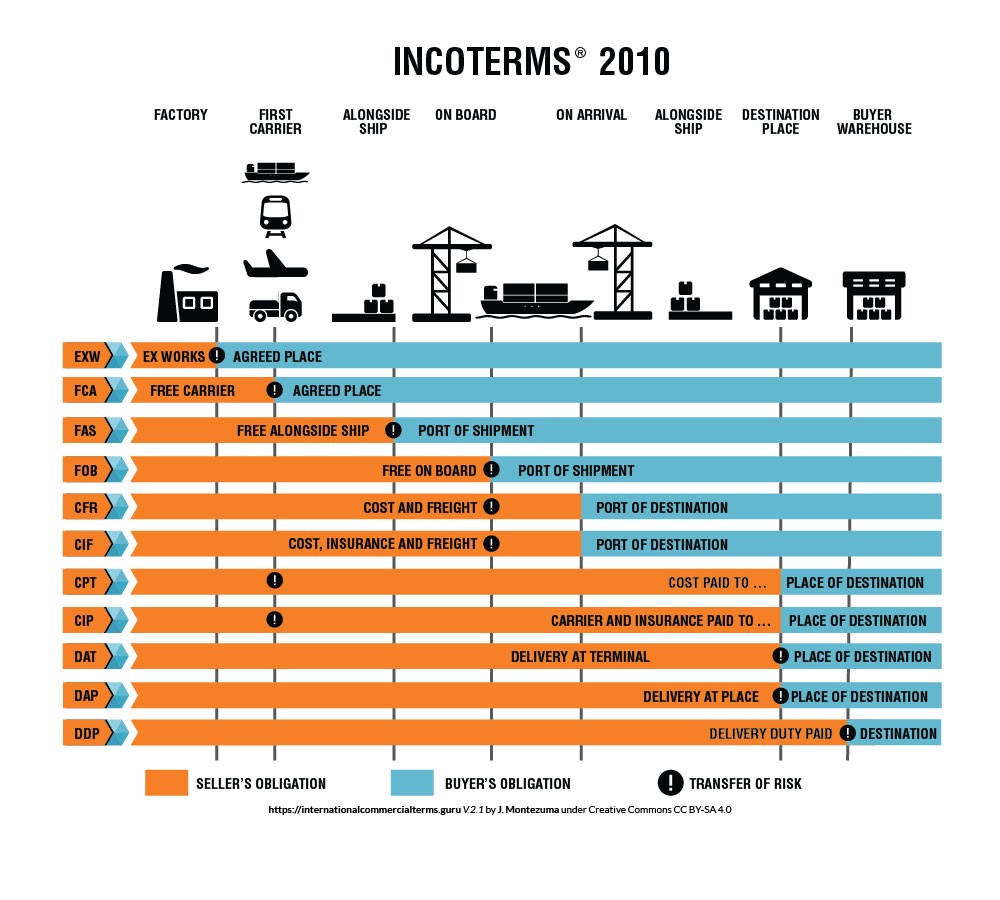
INCOTERMS (2010)
INCOTERMS is an acronym for International Commercial Terms. These are recognized terms in international business transactions. It provides details on the responsibilities of buyers and exporters. The terms are important for the processing of shipping and payment documents during exports. INCOTERMS defines all obligations of buyers and sellers within the logistics chain.
The picture below (source: www.internationalcommercialterms.guru) clearly outlines these obligations under different agreements. It specifies the responsibilities of the buyer and the seller per agreement including the point of transferring the obligations (transfer of risk).
Getting paid
To ensure prompt payment after delivering the specified product to the buyer, it’s important to take into account the following tips:
- Familiarization with the different modes of payments
- Letter of Credit (LC) is a more secured mode of payment
- To receive payment all delivery conditions mentioned on the LC must be satisfied
- Be sure that you can adhere to all the requirements and requested documents listed in the LC
- Discuss the suitability of different options with your bankers / financial advisers
- Undertake due diligence on your buyers before exporting
EXPORT PRICING
To become a successful exporter, one needs the right knowledge about export pricing methods. This includes all items meant for costing and sourcing of products.
Tips for export pricing
- Ensure prices are competitive
- Ensure all export-related and -associated costs are covered
- Know your break-even points
- Set realistic profit margins
- Know the INCOTERMS 2010 for pricing purposes
- Try to negotiate best rates from service providers
- Keep abreast of exchange rates
- Review all of your cost elements periodically
- Include appropriate currencies and HS code(s)
- Include minimum order quantities
INCOTERMS (2010)
Be very clear about the obligations for seller and buyer. This includes spelling out where ownership is transferred between you as an exporter and the importing party. Knowing the INCOTERMS (2010) in detail is indispensable.
Cost categories for export pricing
Make sure to cover all export costs when setting your export pricing. These include local export costs, international export costs and other associated export costs. In more detail, find out all associated costs per category:
LOCAL EXPORT COSTS
All local export costs that should take into account are:
- Sourcing cost
- Packaging and labelling
- Product modification
- Logistics
- Warehousing
- Quality assurance
- Documentation cost
- INCOTERMS 2010
- Product liability insurance or other insurances
- Forwarding cost
- Levies
- Bank charges
- Cost of funds
Click here to read on How to Prevent Bad Debt
INTERNATIONAL EXPORT COSTS
International export costs to consider include:
- Freight costs
- Travel to overseas markets
- Promotional costs
- Import duties/taxes
OTHER ASSOCIATED EXPORT COSTS
Other associated costs for exports are:
- Research into international markets
- International communications
- Productions of export literature (including translations)
Pricing methods
The most common methods for price calculation are the ‘cost-plus’– and ‘top-down’– method. To achieve the best results in setting your export price, we recommend using both methods together. This means that you calculate:
- Outwards your ex-factory price to the end consumer (cost plus)
- From the ideal end consumer price backwards (top-down)
Both methods have their strengths and weaknesses hence, both should be calculated and combined for optimum export pricing balance.
Roles of NEPC concerning export pricing
These include:
- Regular capacity building programmes on costing and pricing for export
- Tailor-made assistance to exporters (office, online media, etc.)
- Provide top-down export market information (international commodity price)
- Provide bottom-up export market information (local commodity market report)
- Provide end-market information to the exporter to aid export pricing
EXPORT FINANCING
As an exporter, ensure you get your export financing right. Keeping in mind that you must fund your export contract.
Five tips for export financing
- Seek help from bankers, financial and export experts
- Explore available government grants and loans
- Know the grants and loans available from local government areas and private parties
- Factoring is a funding facility to consider for increasing your cash flow
- Protect your export proceeds against non-payment risk through Export Credit Insurance
Money needed
Export business requires sustainable funding over some time. The amount of money needed for export is largely dependent on the product and export destination(s). It includes components like marketing and market access, as well as working capital (direct and indirect).
Marketing & market entry costs
Your export budget should cover all costs of marketing your products or services abroad, including the costs of market entry. The product components, requirements of the target market segment and different engagement/publicity needed to draw attention form the basis for marketing and market entry cost.
Specific costs include:
- Hiring competent staff member(s) for the export business
- Regular visits to your targeted export destination(s)
- Provision of samples to bring to the target market
Working capital costs
Additional working capital costs are always involved during the export process. This is the amount of money needed to be available to effectively run the business.
In practice, payment for the contract is received mostly after delivering all of the goods/services.
Thus it is important to keep in mind that you have to make additional direct costs like raw material purchases, packaging, transportation, laboratory services, certification(s).
Some of the indirect costs that should also be taken into account include overheads, personnel, plants and equipment, building.
Payment methods
There are different payment methods available to buyers and sellers.
The main options are:
Documentary credit (e.g. Letter of Credit)
Open account (e.g. advanced payment, cash against the document, deferred payment)
Documentary collections
It is advised to always check and discuss your options for payment with a financial adviser. This is to ensure you to have the right agreements on payment in your export contract.
Funding options
There are numerous funding options available to help you finance your export business:
- Government export incentives
- factoring
- loans (commercial banks/family and friends)
- support from financial institutions
Factoring
Factoring might be an attractive way to help your cash flow. Factoring is a financial transaction where the receivables (such as the invoice) is given to a third party, called a factor for a fee.
Loans
Other ways of funding include loans from friends and family, commercial banks. To access bank loans, one would have to write a bankable proposal.
When writing a bankable proposal take into account the following steps:
- Familiarize yourself with the responsibilities of each financial organization
- Prepare funding request based on their priorities
- Get a copy of their template and use it to develop your proposal
- Formally submit your proposal
Click here to read on How to Start an Electronics Business
Financial institutions
Financial institutions offer a lot of funding options and are therefore a very important source of export financing. Find the main institutions for financial support below.
NIGERIAN EXPORT IMPORT BANK
The Nigerian Export Import (NEXIM) bank offers a wide range of funding options for your export business.
Some of which are:
- Direct Lending Facility (DLF)
- Export Credit Insurance Facility
- Stocking Facility (for manufacturing exporters)
- ECOWAS Interstate Road Transit Scheme
- Foreign Input Facility (for manufacturing exporters)
- Local Input Facility
LEGAL ISSUES
An exporter needs to understand the legal requirements of exports from Nigeria.
Five tips for exporters
- It is recommended to engage an experienced trade lawyer or expert
- Understand the market access conditions for your products
- Protect your intellectual property (IP) rights, if you have one
- Avoid trading on sanctioned/prohibited products
- Check out information on frauds, scams and corrupt practices regularly
Legal & Governmental Regulations
As an exporter, you should be familiar with government regulations. Some of these are:
Export prohibition – exporters should be aware of the list of prohibited items for exports.
Export proceeds repatriation – all proceeds from exports should be repatriated within the stipulated time.
Intellectual Property (IP)
In some cases, you might want to protect your intellectual property. International protection of your IP is extremely important in protecting your business overseas.
Benefits of Exporting
Exporting enables companies to diversify their portfolios and to weather changes in the domestic economy.
Exporting helps small companies grow and become more competitive in all their markets.
For many developing countries, exports also serve the purpose of earning foreign currency with which they can buy essential imports—foreign products that they are not able to manufacture, mine, or grow at home.
Exporting goods and services can also further advance developing nations’ domestic economies.
Exporting products boosts the local economy and helps local businesses increase their revenue.
Increased Sales and Profits
Selling goods and services to a market the company never had before boost sales and increases revenues. Additional foreign sales over the long term, once export development costs have been covered, increase overall profitability.
Enhance Domestic Competitiveness
Most companies become competitive in the domestic market before they venture in the international arena. Being competitive in the domestic market helps companies to acquire some strategies that can help them in the international arena.
Gain Global Market Shares
By going international companies will participate in the global market and gain a piece of their share from the huge international marketplace.
Diversification
Selling to multiple markets allows companies to diversify their business and spread their risk. Companies will not be tied to the changes in the business cycle of the domestic market or one specific country.
Lower Per Unit Costs
Capturing an additional foreign market will usually expand production to meet the foreign demand. Increased production can often lower per-unit costs and lead to greater use of existing capacities.
Compensate for Seasonal Demands
Companies whose products or services are only used at certain seasons domestically may be able to sell their products or services in foreign markets during different seasons.
Create Potential for Company Expansion
Companies who venture into the exporting business usually have to have a presence or representation in the foreign market. This might require additional personnel and thus lead to expansion.
Sell Excess Production Capacity
Companies who have excess production for any reason can probably sell their products in a foreign market and not be forced to give deep discounts or even dispose of their excess production.
Gain New Knowledge and Experience
Going international can yield valuable ideas and information about new technologies, new marketing techniques and foreign competitors. The gains can help a company’s domestic as well as foreign businesses.
Expand Life Cycle of Product
Many products go through various cycles namely introduction, growth, maturity and declining stage that is the end of their usefulness in a specific market. Once the product reaches the final stage, maturity in a given market, the same product can be introduced in a different market where the product was never marketed before.
Exporting Challenges
While the advantages of exporting by far outweigh the disadvantages, small and medium-sized enterprises especially face some challenges when venturing in the international marketplace.
Extra Costs
Because it takes more time to develop extra markets, and the payback periods are longer, the up-front costs for developing new promotional materials, allocating personnel to travel and other administrative costs associated to market the product can strain the meagre financial resources of small size companies.
Product Modification
When exporting, companies may need to modify their products to meet foreign country safety and security codes, and other import restrictions. At a minimum, modification is often necessary to satisfy the importing country’s labelling or packaging requirements.
Financial Risk
Collections of payments using the available methods (open-account, prepayment, consignment, documentary collection and letter of credit) are not only more time-consuming than for domestic sales, but also more complicated. Thus, companies must carefully weigh the financial risk involved in doing international transactions.
Export Licenses and Documentation
Though the trend is toward less export licensing requirements, the fact that some companies have to obtain an export license to export their goods make them less competitive. In many instances, the documentation required to export is more involved than for domestic sales
Market Information
Finding information on foreign markets is unquestionably more difficult and time-consuming than finding information and analyzing domestic markets. In less developed countries, for example, reliable information on business practices, market characteristics, cultural barriers may be unavailable.
Conclusion
Starting an export business in Nigeria comes has both its advantages and disadvantages.
While most people believe exportation should cost you millions of dollars, going in as a broker and leveraging a wide network of local suppliers to supplement the sales of your goods will go a long way in helping you build a successful business that won’t just enable you to generate high revenues in widespread broker commissions but will ensure you contribute positively to Nigeria’s or your own country’s GDP.



There are no comments